

The last couple of dozens of elements added to the Periodic Table have been created synthetically by very high-energy processes. Current research on superatoms (clusters of atoms having properties of a single atom of another element) 10 has led to proposals for multidimensional Periodic Tables to display the relationships. The fundamental insight represented by Mendeleev's 1869 classification framework remains intact, although new interactive online 7and three-dimensional 8, 9 presentations emerge.
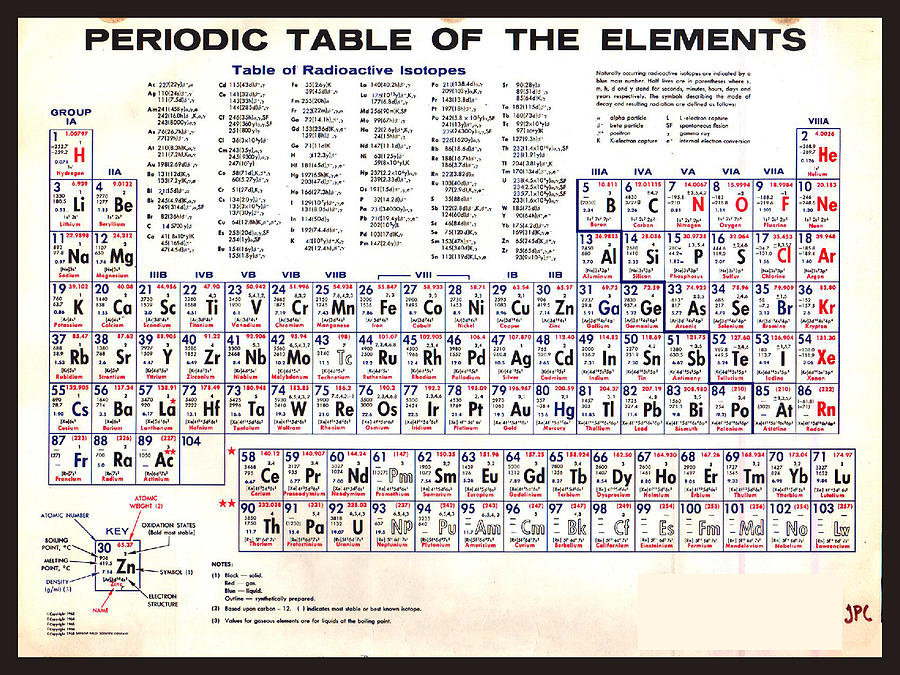
The abiding preeminent position of the Periodic Table in displaying the known elements (now 118) reflects the extent to which the underlying principles on which it is constructed constitute, in effect, a “standard model” for chemistry. Discoveries of new elements and the evolving theoretical understanding of atomic structure eventually resulted in addition of new lanthanide and actinide blocks to the table illustrating the flexibility of the classification system to adapt. the number of nuclear protons, equivalent to the element number), rather than atomic weight, became the recognised basis for ordering its members. The underlying justification for the structure of the Periodic Table emerged only many years later when atomic structure became understood and atomic number (i.e. From his Periodic Table Mendeleev predicted the properties of then unknown elements such as gallium (element 31), germanium (32), scandium (21) and technetium (43), represented by the gaps, which were later discovered, 4 and subsequently others like Henry Moseley 5 continued to extend the Periodic Table through predictions and by filling the gaps. 3 Mendeleev was not the first to publish listings of the known elements in a table but, building on and surpassing the earlier efforts, he rigorously applied the available knowledge of periodic trends in the relationships between the then approximately 60 known elements to produce a chart in which there were gaps at some points. This was an innovative advance in classification which has helped guide the understanding of chemistry and has spurred on advances in the theoretical understanding of atomic structure. The International Year marks the 150th anniversary of the publication by the Russian chemist Dmitry Mendeleev (1834–1907) of his Periodic Table 2 and celebrates the significance and impact of this outstandingly successful chart of the atomic building blocks of matter. The designation by the UN of 2019 as the International Year of the Periodic Table of Chemical Elements 1 provides a timely opportunity to reflect on this warning and consider how best to meet the challenge it presents. We need to ensure that the finite stocks of these are not excessively depleted or used in environmentally damaging ways. The Table reminds us that there are less than 100 stable elements on our planet (as well as a couple of dozens of radioactive ones) from which to derive all the materials that are required for life and for well-being and comfortable living.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
