
Spinal nerves carry somatosensory information into and motor instructions out of the spinal cord. Of note, the accessory nerve innervates the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles, neither of which control muscles used exclusively in the head. The others originating from the brainstem include oculomotor, trochlear, trigeminal, abducens, facial, vestibulocochlear, glossopharyngeal, vagus, spinal accessory, and hypoglossal. The nucleus of the olfactory and optic nerve are located in the forebrain and thalamus, respectively, and are not considered true cranial nerves.
Ten of the cranial nerves originate from the brain stem and mainly control the voluntary movement and structures of the head with some exceptions.
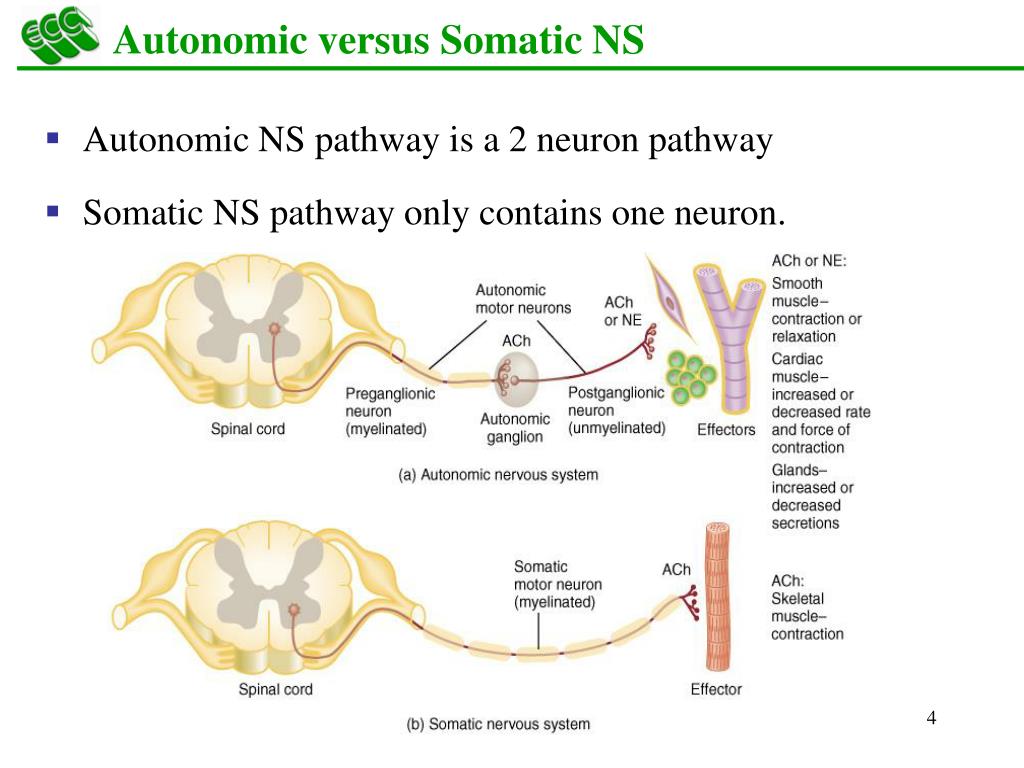
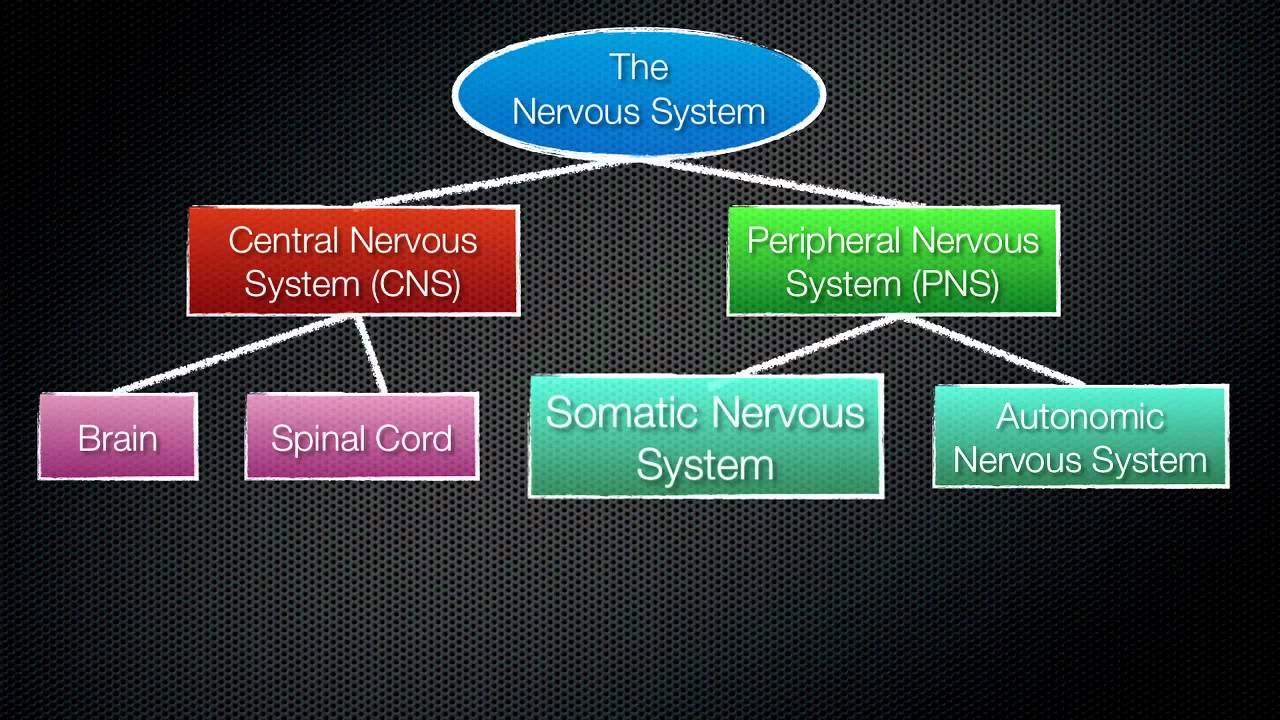
Besides these, there are thousands of other association nerves in the body.Ĭranial nerves are responsible for carrying information in and out of the brain. It is also responsible for the reflex arc, which involves the use of interneurons to perform reflexive actions. The somatic nervous system consists of both afferent (sensory) and efferent (motor) nerves.
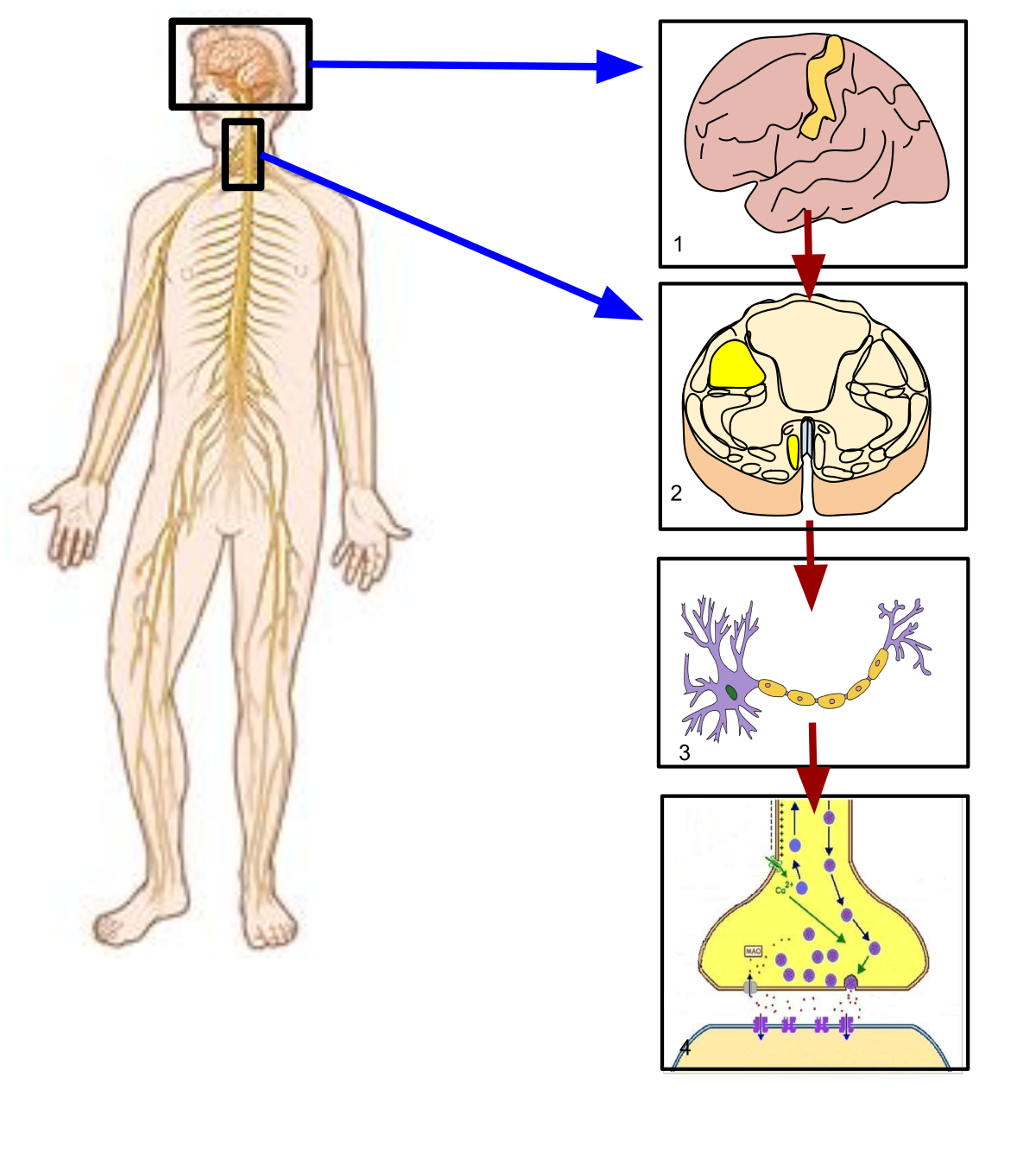
A substantial portion of the peripheral nervous system is the 43 different segments of nerves- 12 pairs of cranial and 31 pairs of spinal nerves, which help us perform daily functions. It is responsible for all the functions we are aware of and can consciously influence, including the movement of our arms legs and other parts of our body. The somatic nervous system is a component of the peripheral nervous system associated with the voluntary control of the body movements via the use of skeletal muscles.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
